Contents
show
Addressing Modes Types
In this article we are going to discuss about addressing modes in computer architecture. In this tutorial we will also learn about different types of addressing modes in computer organization.
In this addressing modes tutorial we are going to cover following topics in detail.
- What is Addressing Mode ?
- Addressing modes type
- Addressing modes examples
- Conclusion.
What is addressing mode?
So lets start with Introduction
What is addressing mode?
In order to understand the concept of addressing modes in computer architecture we need to know about its background detail. Actually When an instruction is fetched from memory then it is stored in an Instruction Register.
This Instruction register is connected to a decoder. Decoder decodes this instruction. Then instruction format has mainly three parts as shown in following figure.
This Instruction register is connected to a decoder. Decoder decodes this instruction. Then instruction format has mainly three parts as shown in following figure.
|
Mode Bit
(15)
|
OPCODE
(14,13,12)
|
Address Field (11……………,1,0)
|
This is for 16 bits instruction. The address part provides the information about the effective address of the operand. Computing the effecting address of the operand is an important task to complete the execution of the instruction.
So if we have to define address mode the we can say that addressing mode is a way or technique for specifying the address of the operand it means at which address the operand is stored in memory.
So if we have to define address mode the we can say that addressing mode is a way or technique for specifying the address of the operand it means at which address the operand is stored in memory.
Addressing modes types
All computer architectures provide more than one of these addressing modes. The question arises as to how the control unit can determine which addressing mode is being used in a particular instruction. Several approaches are used. Often, different opcode will use different addressing modes.
The value of the mode field determines which addressing mode is to be used. What is the interpretation of effective address? In a system without virtual memory, the effective address will be either the main memory address or a register.
In a virtual memory system, the effective address is a virtual address or a register. The actual mapping to a physical address is a function of the paging mechanism and is invisible to the programmer.
There are following types of addressing modes.
(1) Immediate Addressing Mode
The simplest form of addressing is immediate addressing mode, in which the operand is itself present in the instruction:
The address field part of the instruction is nothing but the operand itself. Immediate addressing mode can be used to define and use constants or set initial values of variables. Immediate addressing mode example is explained here
Example : Consider the instruction LOAD 5. So in this instruction 5 is itself is an operand.
The advantage of immediate addressing mode is that no memory reference other than the instruction fetch is required to obtain the operand.
The disadvantage of immediate addressing mode is that the size of the number is restricted to the size of the address field, which, in most instruction sets, is small compared with the word length.
The disadvantage of immediate addressing mode is that the size of the number is restricted to the size of the address field, which, in most instruction sets, is small compared with the word length.
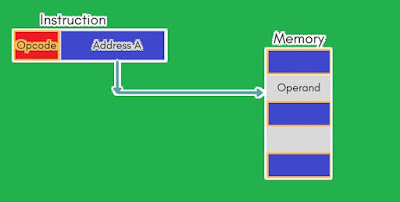
(2) Direct Addressing Mode
When we simply say direct address mode then it is understood that operand is stored in the memory not in register. A very simple form of addressing is direct addressing, in which the address field contains the effective address of the operand.
This mode is also known as absolute addressing mode. It requires only one memory reference and no special calculation.
Figure 1: Direct Addressing Mode
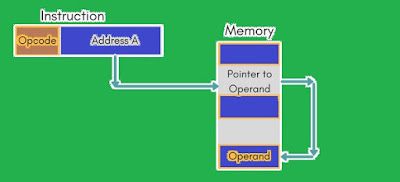
(3) Indirect Addressing Mode
With direct addressing, the length of the address field is usually less than the word length, thus limiting the address range.
One solution is to have the address field refer to the address of a word in memory, which in turn contains a full-length address of the operand. This is known as indirect addressing mode.
One solution is to have the address field refer to the address of a word in memory, which in turn contains a full-length address of the operand. This is known as indirect addressing mode.
Figure 2: Indirect Addressing Mode
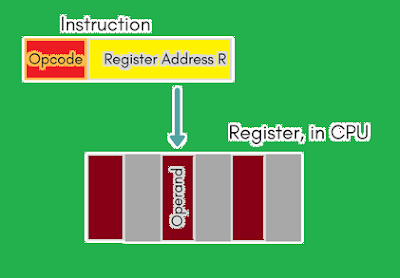
(4) Register Direct Addressing Mode
Register direct addressing is similar to direct addressing. The only difference is that the address field refers to a register rather than a main memory address.
It means operand is stored in the register as per specified by the address field of the instruction. This register is inside the cpu.
It means operand is stored in the register as per specified by the address field of the instruction. This register is inside the cpu.
The advantages of registers direct addressing are that only a small address field is needed in the instruction and no memory reference is required.
The disadvantage of registers direct addressing is that the address space is very limited.
The disadvantage of registers direct addressing is that the address space is very limited.
Figure 3: Register Direct Mode
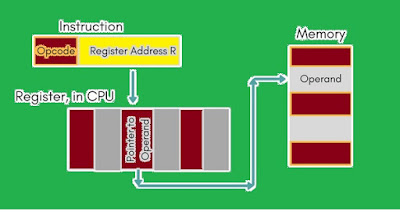
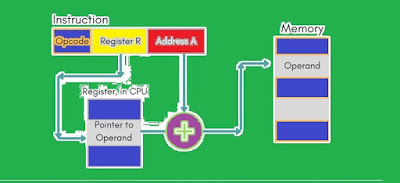
(5) Register Indirect Addressing Mode
Register indirect addressing is similar to indirect addressing, except that the address meaning field refers to a register instead of a memory location. It requires only one memory reference and no special calculation.
Register indirect addressing mode uses one less memory reference than indirect addressing. Because, the first information is available in a register which is nothing but a memory address and at that memory address the operand is stored.
Figure 4 : Register Indirect Mode
(6) Displacement Addressing Mode
A very powerful mode of addressing combines the capabilities of direct addressing and register indirect addressing, which is broadly categorized as displacement addressing:
EA = A + (R)
Displacement addressing requires that the instruction have two address fields, at least one of which is explicit. The value contained in one address field (value = A) is used directly.
The other address field, or an implicit reference based on opcode, refers to a register whose contents are added to A to produce the effective address.
The other address field, or an implicit reference based on opcode, refers to a register whose contents are added to A to produce the effective address.
Figure 5: Displacement Addressing Mode
Three of the most common use of displacement addressing are:
• Relative addressing
• Base-register addressing
• Indexing
6.1 Relative Addressing Mode
For relative addressing, the implicitly referenced register is the program counter (PC). That is, the current instruction address is added to the address field to produce the EA. Thus, the effective address is a displacement relative to the address of the instruction.
6.2. Base-Register Addressing Mode
The reference register contains a memory address, and the address field contains a displacement from that address. The register reference may be explicit or implicit.
In some implementation, a single segment/base register is employed and is used implicitly. In others, the programmer may choose a register to hold the base address of a segment, and the instruction must reference it explicitly.
I have also explained this article in the following video. So students are advised to watch this video to understand the concept of addressing mode.
In some implementation, a single segment/base register is employed and is used implicitly. In others, the programmer may choose a register to hold the base address of a segment, and the instruction must reference it explicitly.
I have also explained this article in the following video. So students are advised to watch this video to understand the concept of addressing mode.
Addressing mode example
At memory address 200, a two instruction LOAD AC is stored. At location 201 the address stored is 500. At location 202 next instruction is stored. The following numbers are stored at different memory location as shown in this table.
|
Memory Location ( Address)
|
Memory Content
|
|
399
|
450
|
|
400
|
700
|
|
500
|
800
|
|
600
|
900
|
|
702
|
325
|
|
800
|
300
|
If the content of PC is 200, while the content of register R1 is 400. XR register is 100 .If all the numbers and address in decimal number find out the content of AC and effective address for the following addressing modes.
(a) Direct Addressing (b) Indirect Addressing (c) Relative Addressing (d) Indexed Addressing (e) Register Indirect Addressing.
Solution :
(1) Direct Addressing: Since it is given that address field of instruction is 500 so ih direct mode this value itself is an Effective Address.
So Effective Address = 500 and
Operand = 800.
(2) Indirect Mode
Effective Address = M[500]=800
Operand = M[800]= 300
(3) Relative Addressing Mode:
Effective Address = PC + 500 = 202 + 500 =702
Operand = 325
(4) Indexed Address Mode
Effective Address = Base Register Value + 500
= 100 + 500 = 600
Operand = M[600] = 900
(5) Register Indirect Mode
Effective Address = M[R1]= 400
Operand = M[400]= 700.
I hope that this article will be helpful for computer science students in understanding the concepts of addressing modes in computer architecture. Dear readers your suggestions and comment are really valuable for us to improve the quality of the article. so please give your feedback in form of comment.